空间复杂度¶
空间复杂度(space complexity)用于衡量算法占用内存空间随着数据量变大时的增长趋势。这个概念与时间复杂度非常类似,只需将“运行时间”替换为“占用内存空间”。
算法相关空间¶
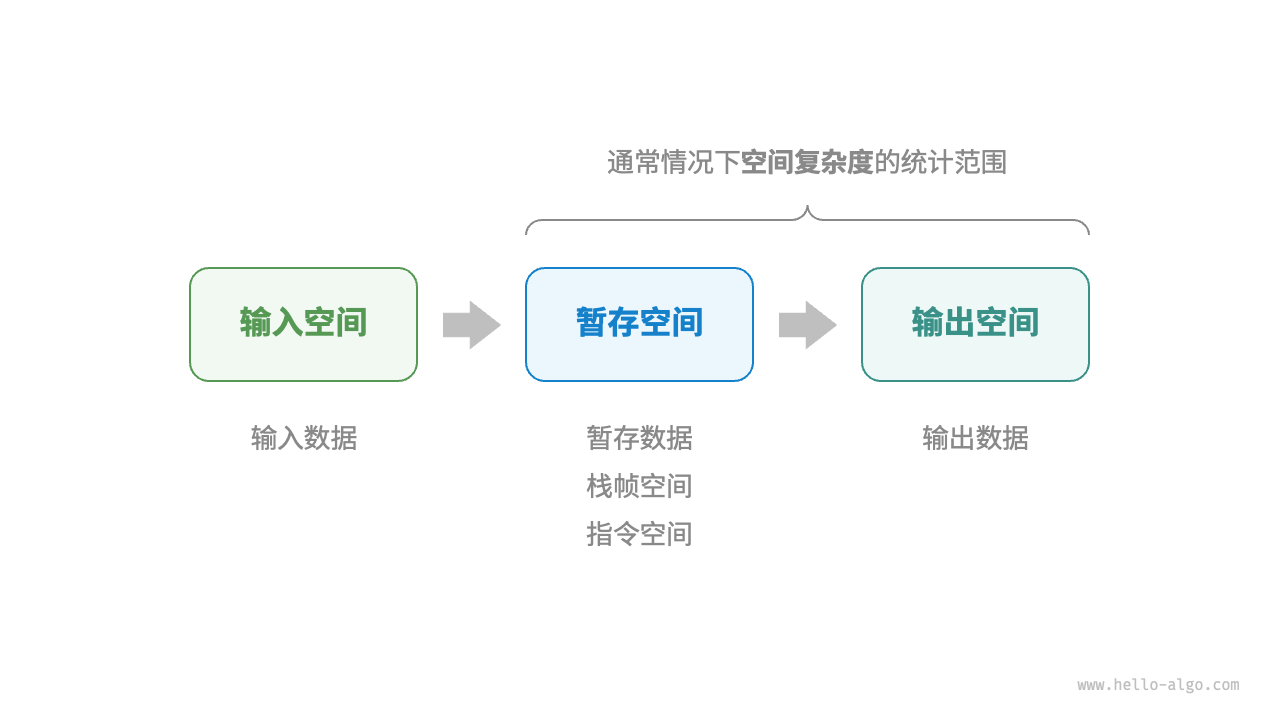
算法在运行过程中使用的内存空间主要包括以下几种。
- 输入空间:用于存储算法的输入数据。
- 暂存空间:用于存储算法在运行过程中的变量、对象、函数上下文等数据。
- 输出空间:用于存储算法的输出数据。
一般情况下,空间复杂度的统计范围是“暂存空间”加上“输出空间”。
暂存空间可以进一步划分为三个部分。
- 暂存数据:用于保存算法运行过程中的各种常量、变量、对象等。
- 栈帧空间:用于保存调用函数的上下文数据。系统在每次调用函数时都会在栈顶部创建一个栈帧,函数返回后,栈帧空间会被释放。
- 指令空间:用于保存编译后的程序指令,在实际统计中通常忽略不计。
在分析一段程序的空间复杂度时,我们通常统计暂存数据、栈帧空间和输出数据三部分,如下图所示。
相关代码如下:
=== "Python"
```python title=""
class Node:
"""类"""
def __init__(self, x: int):
self.val: int = x # 节点值
self.next: Node | None = None # 指向下一节点的引用
def function() -> int:
"""函数"""
# 执行某些操作...
return 0
def algorithm(n) -> int: # 输入数据
A = 0 # 暂存数据(常量,一般用大写字母表示)
b = 0 # 暂存数据(变量)
node = Node(0) # 暂存数据(对象)
c = function() # 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return A + b + c # 输出数据
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title=""
/* 结构体 */
struct Node {
int val;
Node *next;
Node(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
};
/* 函数 */
int func() {
// 执行某些操作...
return 0;
}
int algorithm(int n) { // 输入数据
const int a = 0; // 暂存数据(常量)
int b = 0; // 暂存数据(变量)
Node* node = new Node(0); // 暂存数据(对象)
int c = func(); // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c; // 输出数据
}
```
=== "Java"
```java title=""
/* 类 */
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node(int x) { val = x; }
}
/* 函数 */
int function() {
// 执行某些操作...
return 0;
}
int algorithm(int n) { // 输入数据
final int a = 0; // 暂存数据(常量)
int b = 0; // 暂存数据(变量)
Node node = new Node(0); // 暂存数据(对象)
int c = function(); // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c; // 输出数据
}
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title=""
/* 类 */
class Node(int x) {
int val = x;
Node next;
}
/* 函数 */
int Function() {
// 执行某些操作...
return 0;
}
int Algorithm(int n) { // 输入数据
const int a = 0; // 暂存数据(常量)
int b = 0; // 暂存数据(变量)
Node node = new(0); // 暂存数据(对象)
int c = Function(); // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c; // 输出数据
}
```
=== "Go"
```go title=""
/* 结构体 */
type node struct {
val int
next *node
}
/* 创建 node 结构体 */
func newNode(val int) *node {
return &node{val: val}
}
/* 函数 */
func function() int {
// 执行某些操作...
return 0
}
func algorithm(n int) int { // 输入数据
const a = 0 // 暂存数据(常量)
b := 0 // 暂存数据(变量)
newNode(0) // 暂存数据(对象)
c := function() // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c // 输出数据
}
```
=== "Swift"
```swift title=""
/* 类 */
class Node {
var val: Int
var next: Node?
init(x: Int) {
val = x
}
}
/* 函数 */
func function() -> Int {
// 执行某些操作...
return 0
}
func algorithm(n: Int) -> Int { // 输入数据
let a = 0 // 暂存数据(常量)
var b = 0 // 暂存数据(变量)
let node = Node(x: 0) // 暂存数据(对象)
let c = function() // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c // 输出数据
}
```
=== "JS"
```javascript title=""
/* 类 */
class Node {
val;
next;
constructor(val) {
this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val; // 节点值
this.next = null; // 指向下一节点的引用
}
}
/* 函数 */
function constFunc() {
// 执行某些操作
return 0;
}
function algorithm(n) { // 输入数据
const a = 0; // 暂存数据(常量)
let b = 0; // 暂存数据(变量)
const node = new Node(0); // 暂存数据(对象)
const c = constFunc(); // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c; // 输出数据
}
```
=== "TS"
```typescript title=""
/* 类 */
class Node {
val: number;
next: Node | null;
constructor(val?: number) {
this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val; // 节点值
this.next = null; // 指向下一节点的引用
}
}
/* 函数 */
function constFunc(): number {
// 执行某些操作
return 0;
}
function algorithm(n: number): number { // 输入数据
const a = 0; // 暂存数据(常量)
let b = 0; // 暂存数据(变量)
const node = new Node(0); // 暂存数据(对象)
const c = constFunc(); // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c; // 输出数据
}
```
=== "Dart"
```dart title=""
/* 类 */
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node(this.val, [this.next]);
}
/* 函数 */
int function() {
// 执行某些操作...
return 0;
}
int algorithm(int n) { // 输入数据
const int a = 0; // 暂存数据(常量)
int b = 0; // 暂存数据(变量)
Node node = Node(0); // 暂存数据(对象)
int c = function(); // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c; // 输出数据
}
```
=== "Rust"
```rust title=""
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
/* 结构体 */
struct Node {
val: i32,
next: Option<Rc<RefCell<Node>>>,
}
/* 创建 Node 结构体 */
impl Node {
fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
Self { val: val, next: None }
}
}
/* 函数 */
fn function() -> i32 {
// 执行某些操作...
return 0;
}
fn algorithm(n: i32) -> i32 { // 输入数据
const a: i32 = 0; // 暂存数据(常量)
let mut b = 0; // 暂存数据(变量)
let node = Node::new(0); // 暂存数据(对象)
let c = function(); // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c; // 输出数据
}
```
=== "C"
```c title=""
/* 函数 */
int func() {
// 执行某些操作...
return 0;
}
int algorithm(int n) { // 输入数据
const int a = 0; // 暂存数据(常量)
int b = 0; // 暂存数据(变量)
int c = func(); // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c; // 输出数据
}
```
=== "Kotlin"
```kotlin title=""
/* 类 */
class Node(var _val: Int) {
var next: Node? = null
}
/* 函数 */
fun function(): Int {
// 执行某些操作...
return 0
}
fun algorithm(n: Int): Int { // 输入数据
val a = 0 // 暂存数据(常量)
var b = 0 // 暂存数据(变量)
val node = Node(0) // 暂存数据(对象)
val c = function() // 栈帧空间(调用函数)
return a + b + c // 输出数据
}
```
=== "Ruby"
```ruby title=""
### 类 ###
class Node
attr_accessor :val # 节点值
attr_accessor :next # 指向下一节点的引用
def initialize(x)
@val = x
end
end
### 函数 ###
def function
# 执行某些操作...
0
end
### 算法 ###
def algorithm(n) # 输入数据
a = 0 # 暂存数据(常量)
b = 0 # 暂存数据(变量)
node = Node.new(0) # 暂存数据(对象)
c = function # 栈帧空间(调用函数)
a + b + c # 输出数据
end
```
=== "Zig"
```zig title=""
```
推算方法¶
空间复杂度的推算方法与时间复杂度大致相同,只需将统计对象从“操作数量”转为“使用空间大小”。
而与时间复杂度不同的是,我们通常只关注最差空间复杂度。这是因为内存空间是一项硬性要求,我们必须确保在所有输入数据下都有足够的内存空间预留。
观察以下代码,最差空间复杂度中的“最差”有两层含义。
- 以最差输入数据为准:当 $n < 10$ 时,空间复杂度为 $O(1)$ ;但当 $n > 10$ 时,初始化的数组
nums占用 $O(n)$ 空间,因此最差空间复杂度为 $O(n)$ 。 - 以算法运行中的峰值内存为准:例如,程序在执行最后一行之前,占用 $O(1)$ 空间;当初始化数组
nums时,程序占用 $O(n)$ 空间,因此最差空间复杂度为 $O(n)$ 。
=== "Python"
```python title=""
def algorithm(n: int):
a = 0 # O(1)
b = [0] * 10000 # O(1)
if n > 10:
nums = [0] * n # O(n)
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title=""
void algorithm(int n) {
int a = 0; // O(1)
vector<int> b(10000); // O(1)
if (n > 10)
vector<int> nums(n); // O(n)
}
```
=== "Java"
```java title=""
void algorithm(int n) {
int a = 0; // O(1)
int[] b = new int[10000]; // O(1)
if (n > 10)
int[] nums = new int[n]; // O(n)
}
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title=""
void Algorithm(int n) {
int a = 0; // O(1)
int[] b = new int[10000]; // O(1)
if (n > 10) {
int[] nums = new int[n]; // O(n)
}
}
```
=== "Go"
```go title=""
func algorithm(n int) {
a := 0 // O(1)
b := make([]int, 10000) // O(1)
var nums []int
if n > 10 {
nums := make([]int, n) // O(n)
}
fmt.Println(a, b, nums)
}
```
=== "Swift"
```swift title=""
func algorithm(n: Int) {
let a = 0 // O(1)
let b = Array(repeating: 0, count: 10000) // O(1)
if n > 10 {
let nums = Array(repeating: 0, count: n) // O(n)
}
}
```
=== "JS"
```javascript title=""
function algorithm(n) {
const a = 0; // O(1)
const b = new Array(10000); // O(1)
if (n > 10) {
const nums = new Array(n); // O(n)
}
}
```
=== "TS"
```typescript title=""
function algorithm(n: number): void {
const a = 0; // O(1)
const b = new Array(10000); // O(1)
if (n > 10) {
const nums = new Array(n); // O(n)
}
}
```
=== "Dart"
```dart title=""
void algorithm(int n) {
int a = 0; // O(1)
List<int> b = List.filled(10000, 0); // O(1)
if (n > 10) {
List<int> nums = List.filled(n, 0); // O(n)
}
}
```
=== "Rust"
```rust title=""
fn algorithm(n: i32) {
let a = 0; // O(1)
let b = [0; 10000]; // O(1)
if n > 10 {
let nums = vec![0; n as usize]; // O(n)
}
}
```
=== "C"
```c title=""
void algorithm(int n) {
int a = 0; // O(1)
int b[10000]; // O(1)
if (n > 10)
int nums[n] = {0}; // O(n)
}
```
=== "Kotlin"
```kotlin title=""
fun algorithm(n: Int) {
val a = 0 // O(1)
val b = IntArray(10000) // O(1)
if (n > 10) {
val nums = IntArray(n) // O(n)
}
}
```
=== "Ruby"
```ruby title=""
def algorithm(n)
a = 0 # O(1)
b = Array.new(10000) # O(1)
nums = Array.new(n) if n > 10 # O(n)
end
```
=== "Zig"
```zig title=""
```
在递归函数中,需要注意统计栈帧空间。观察以下代码:
=== "Python"
```python title=""
def function() -> int:
# 执行某些操作
return 0
def loop(n: int):
"""循环的空间复杂度为 O(1)"""
for _ in range(n):
function()
def recur(n: int):
"""递归的空间复杂度为 O(n)"""
if n == 1:
return
return recur(n - 1)
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title=""
int func() {
// 执行某些操作
return 0;
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
void loop(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
func();
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
void recur(int n) {
if (n == 1) return;
return recur(n - 1);
}
```
=== "Java"
```java title=""
int function() {
// 执行某些操作
return 0;
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
void loop(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
function();
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
void recur(int n) {
if (n == 1) return;
return recur(n - 1);
}
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title=""
int Function() {
// 执行某些操作
return 0;
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
void Loop(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Function();
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
int Recur(int n) {
if (n == 1) return 1;
return Recur(n - 1);
}
```
=== "Go"
```go title=""
func function() int {
// 执行某些操作
return 0
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
func loop(n int) {
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
function()
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
func recur(n int) {
if n == 1 {
return
}
recur(n - 1)
}
```
=== "Swift"
```swift title=""
@discardableResult
func function() -> Int {
// 执行某些操作
return 0
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
func loop(n: Int) {
for _ in 0 ..< n {
function()
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
func recur(n: Int) {
if n == 1 {
return
}
recur(n: n - 1)
}
```
=== "JS"
```javascript title=""
function constFunc() {
// 执行某些操作
return 0;
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
function loop(n) {
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
constFunc();
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
function recur(n) {
if (n === 1) return;
return recur(n - 1);
}
```
=== "TS"
```typescript title=""
function constFunc(): number {
// 执行某些操作
return 0;
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
function loop(n: number): void {
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
constFunc();
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
function recur(n: number): void {
if (n === 1) return;
return recur(n - 1);
}
```
=== "Dart"
```dart title=""
int function() {
// 执行某些操作
return 0;
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
void loop(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
function();
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
void recur(int n) {
if (n == 1) return;
return recur(n - 1);
}
```
=== "Rust"
```rust title=""
fn function() -> i32 {
// 执行某些操作
return 0;
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
fn loop(n: i32) {
for i in 0..n {
function();
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
fn recur(n: i32) {
if n == 1 {
return;
}
recur(n - 1);
}
```
=== "C"
```c title=""
int func() {
// 执行某些操作
return 0;
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
void loop(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
func();
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
void recur(int n) {
if (n == 1) return;
return recur(n - 1);
}
```
=== "Kotlin"
```kotlin title=""
fun function(): Int {
// 执行某些操作
return 0
}
/* 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) */
fun loop(n: Int) {
for (i in 0..<n) {
function()
}
}
/* 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) */
fun recur(n: Int) {
if (n == 1) return
return recur(n - 1)
}
```
=== "Ruby"
```ruby title=""
def function
# 执行某些操作
0
end
### 循环的空间复杂度为 O(1) ###
def loop(n)
(0...n).each { function }
end
### 递归的空间复杂度为 O(n) ###
def recur(n)
return if n == 1
recur(n - 1)
end
```
=== "Zig"
```zig title=""
```
函数 loop() 和 recur() 的时间复杂度都为 $O(n)$ ,但空间复杂度不同。
- 函数
loop()在循环中调用了 $n$ 次function(),每轮中的function()都返回并释放了栈帧空间,因此空间复杂度仍为 $O(1)$ 。 - 递归函数
recur()在运行过程中会同时存在 $n$ 个未返回的recur(),从而占用 $O(n)$ 的栈帧空间。
常见类型¶
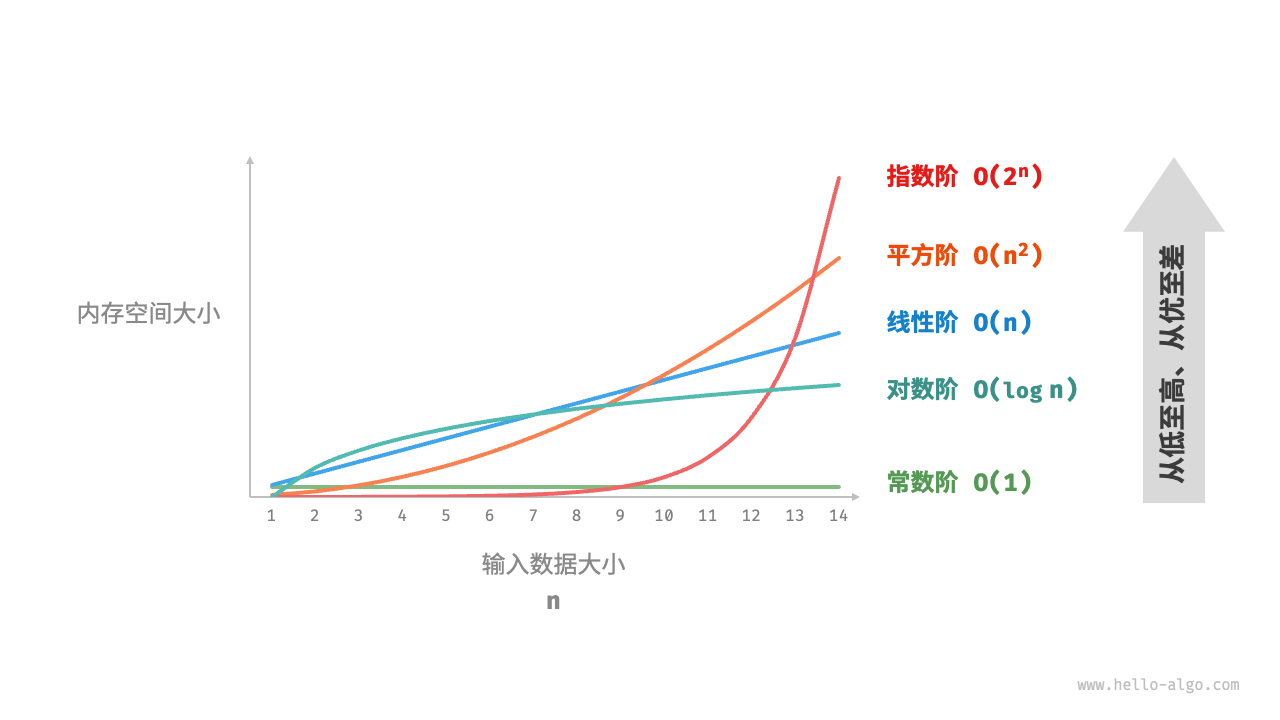
设输入数据大小为 $n$ ,下图展示了常见的空间复杂度类型(从低到高排列)。
$$ \begin{aligned} O(1) < O(\log n) < O(n) < O(n^2) < O(2^n) \newline \text{常数阶} < \text{对数阶} < \text{线性阶} < \text{平方阶} < \text{指数阶} \end{aligned} $$
常数阶 $O(1)$¶
常数阶常见于数量与输入数据大小 $n$ 无关的常量、变量、对象。
需要注意的是,在循环中初始化变量或调用函数而占用的内存,在进入下一循环后就会被释放,因此不会累积占用空间,空间复杂度仍为 $O(1)$ :
[file]{space_complexity}-[class]{}-[func]{constant}
线性阶 $O(n)$¶
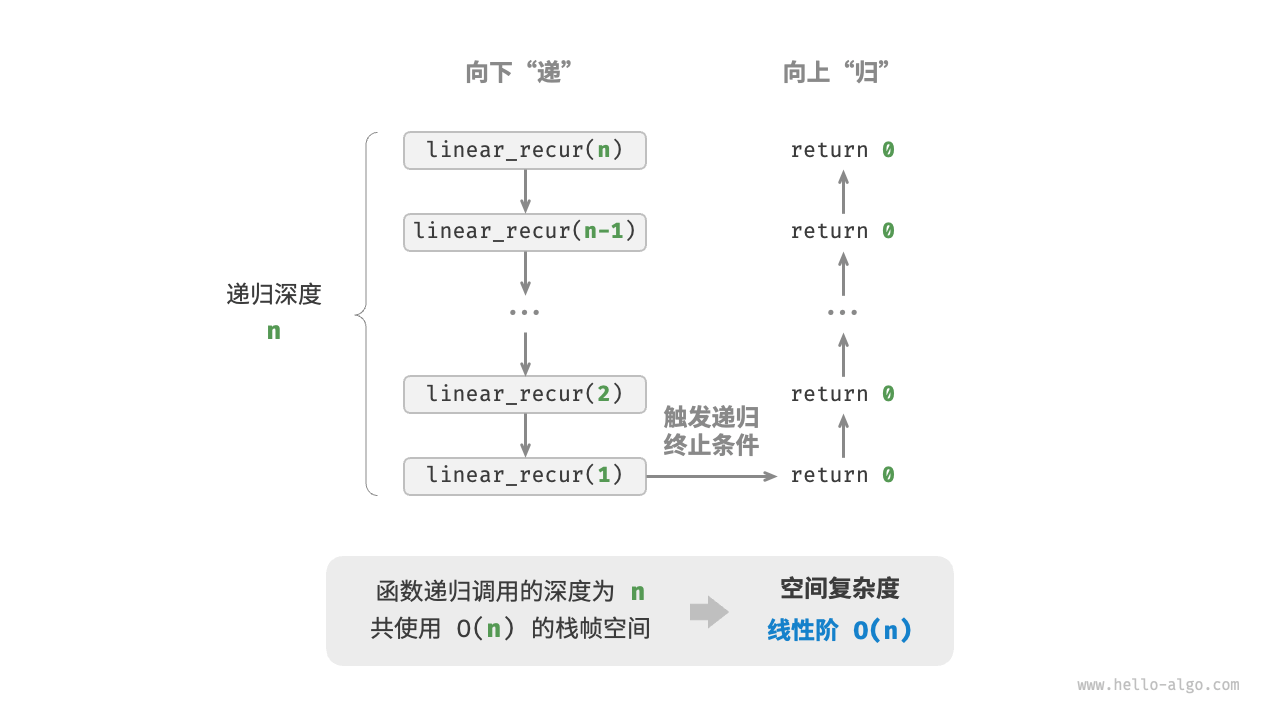
线性阶常见于元素数量与 $n$ 成正比的数组、链表、栈、队列等:
[file]{space_complexity}-[class]{}-[func]{linear}
如下图所示,此函数的递归深度为 $n$ ,即同时存在 $n$ 个未返回的 linear_recur() 函数,使用 $O(n)$ 大小的栈帧空间:
[file]{space_complexity}-[class]{}-[func]{linear_recur}
平方阶 $O(n^2)$¶
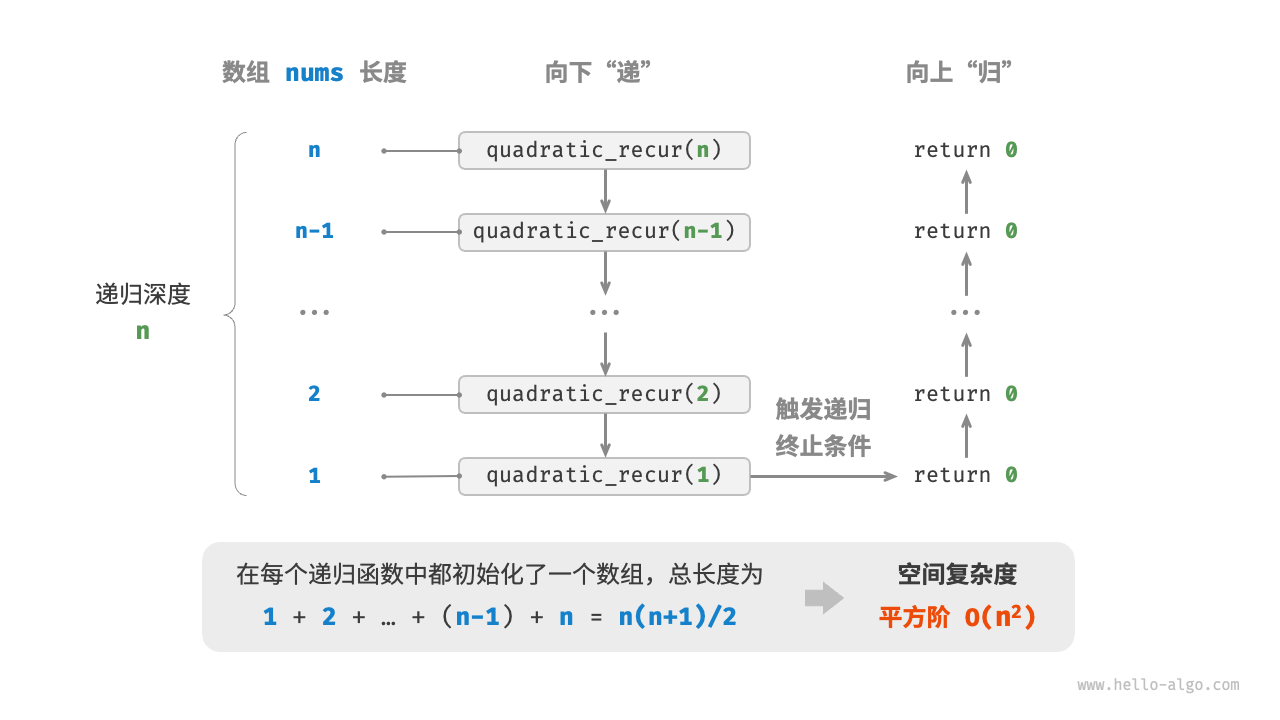
平方阶常见于矩阵和图,元素数量与 $n$ 成平方关系:
[file]{space_complexity}-[class]{}-[func]{quadratic}
如下图所示,该函数的递归深度为 $n$ ,在每个递归函数中都初始化了一个数组,长度分别为 $n$、$n-1$、$\dots$、$2$、$1$ ,平均长度为 $n / 2$ ,因此总体占用 $O(n^2)$ 空间:
[file]{space_complexity}-[class]{}-[func]{quadratic_recur}
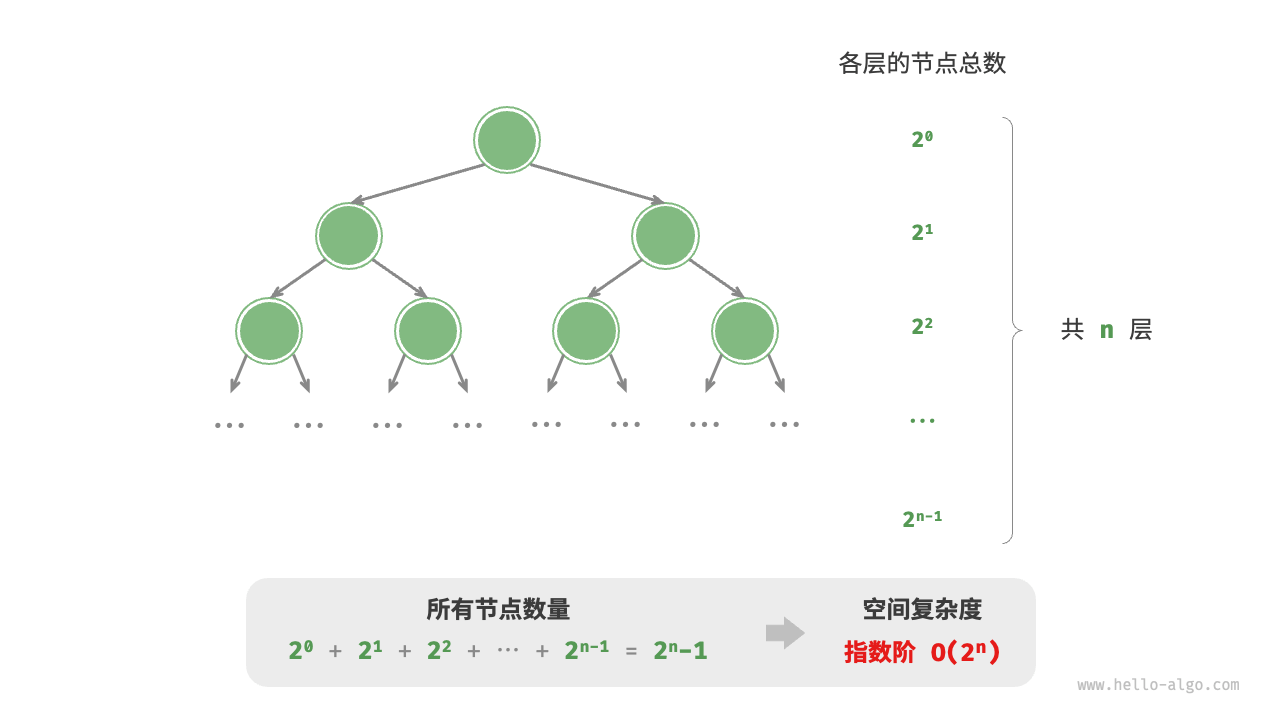
指数阶 $O(2^n)$¶
指数阶常见于二叉树。观察下图,层数为 $n$ 的“满二叉树”的节点数量为 $2^n - 1$ ,占用 $O(2^n)$ 空间:
[file]{space_complexity}-[class]{}-[func]{build_tree}
对数阶 $O(\log n)$¶
对数阶常见于分治算法。例如归并排序,输入长度为 $n$ 的数组,每轮递归将数组从中点处划分为两半,形成高度为 $\log n$ 的递归树,使用 $O(\log n)$ 栈帧空间。
再例如将数字转化为字符串,输入一个正整数 $n$ ,它的位数为 $\lfloor \log_{10} n \rfloor + 1$ ,即对应字符串长度为 $\lfloor \log_{10} n \rfloor + 1$ ,因此空间复杂度为 $O(\log_{10} n + 1) = O(\log n)$ 。
权衡时间与空间¶
理想情况下,我们希望算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度都能达到最优。然而在实际情况中,同时优化时间复杂度和空间复杂度通常非常困难。
降低时间复杂度通常需要以提升空间复杂度为代价,反之亦然。我们将牺牲内存空间来提升算法运行速度的思路称为“以空间换时间”;反之,则称为“以时间换空间”。
选择哪种思路取决于我们更看重哪个方面。在大多数情况下,时间比空间更宝贵,因此“以空间换时间”通常是更常用的策略。当然,在数据量很大的情况下,控制空间复杂度也非常重要。